Table of Contents
In order to stay ahead in the rapidly changing world of business, you must consider some extraordinary strategies. Simply having an outstanding product or service is insufficient in today’s changing competitive landscape. To become a lead runner, companies must focus on enhancing operational efficiency and flexibility within their workflow processes.
Here BPM or business process management comes into picture. It’s a perfect technique to identify, formulate and progressively upgrade processes as required. This helps in achieving overall organizational goals.
This blog post will offer a basic introduction to Business project management (BPM), highlighting its importance in driving the progress of startups, businesses and enterprises.
What is BPM?
The field of Business Process Management, known as BPM for short, strives to enhance a company’s efficacy by effectively managing and simplifying its procedures. There are various processes that it can enhance from the acquisition of customers and processing orders to reporting finances and ensuring efficient supply chain management.
BPM involves examining current workflows, creating more efficient alternatives, implementing alterations, and constantly monitoring results in order to ensure ongoing improvement.
Business Process Management Strategy
A comprehensive and structured approach implemented by organizations is the Business Process Management (BPM) strategy to manage, optimize, and continuously enhance their business processes. The primary goal of this plan is process alignment with organizational goals and objectives that guarantee efficient operations which are both effective as well as adaptable in the face of changes. Below we provide a detailed understanding regarding what it means for an organization to adopt a BPM strategy.
Key Components of the BPM strategy
Setting Objectives:
The objectives and aims of the BPM initiative should be clearly outlined, including goals such as boosting effectiveness, diminishing expenses, elevating client satisfaction to achieving compliance with regulatory standards.
Process identification and prioritization:
Identify the key business processes that greatly influence the achievements of an organization. Prioritize these operations according to their importance, ongoing performance, setbacks and potential for improvement.
Engagement of Stakeholders:
To ensure better collaboration and support for BPM strategies, it is essential to engage all relevant stakeholders such as employees, management, and customers in the BPM strategy. Effective stakeholder engagement facilitates taking into account diverse perspectives and needs of each party involved.
Process mapping and documenting:
Thoroughly map the current processes, comprehensively noting every action taken, position involved, and obligation. This effectively defines the current state of affairs and establishes a base for identifying potential improvements.
Technology and Tool Selection:
Select BPM tools and technologies that are suitable for fulfilling the requirements of your organization. These tools must facilitate process modeling, automation, monitoring as well as analysis.
Implementation Plan:
Create a comprehensive strategy for executing the redesign and automation of processes. The plan must include specific steps, complete with timelines, resource distribution plans, approaches to reduce risk factors along the way and key milestones that serve as progress indicators.
Change Management:
Develop a strategy for managing change that specifically targets the human factors of process modification. This will involve providing staff with appropriate training, communicating changes in an efficient manner, and handling any opposition to these alterations in a proactive way.
Monitoring and Measurement:
To monitor the efficiency of redesigned procedures, set up metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). Consistent monitoring aids in detecting discrepancies, evaluating alterations’ effects, and facilitating data-based choices.
Continuous Improvement:
Develop a mindset of constant improvement through regular evaluation and optimization of processes. Use observations from monitoring efforts and feedback to make iterative upgrades to the procedures.
What is the importance of BPM?
The implementation of BPM is essential for organizations to systematically manage and enhance their business procedures, guaranteeing efficiency, effectiveness, and congruence with strategic objectives.
Utilizing BPM enables companies to optimize operations while cutting costs; cultivating customer satisfaction through enhanced innovation in response to fluid market conditions. In addition, utilizing a culture of continuous improvement will further aid companies in achieving regulatory compliance as well as mitigating risks associated with inefficient manual processes.
Efficiency improvement: To enhance efficiency, processes are streamlined to eliminate any instances of waste and redundancy.
Cost Reduction: By using automation and optimizing processes, operational costs are minimized.
Improved Agility: Facilitates swift adjustment to alterations in the market and customer requirements.
Enhanced customer service: Improving service delivery and customer interactions leads to enhanced customer satisfaction.
Continuous improvement: It fosters persistent enhancement and novelty in processes.
Risk management: This aims to reduce mistakes and guarantee adherence to regulatory norms.
Improved Visibility: Offers up-to-the-minute analysis of process efficiency and obstacles.
Employee productivity: Automation increases employee productivity by allowing them to dedicate more time towards tasks of a higher value.
Strategic alignment: This ensures that organizational processes are in sync with established goals and objectives.
Different types of BPM
The three main types of BPM are classified as follows:
Human-centric BPM:
BPM with a human-centric approach prioritizes processes that involve significant interaction between people. These could be workflows like employee onboarding, customer service protocols or approval procedures which necessitate human decision making, cooperation and involvement. By making these tasks more efficient, businesses can boost employee efficiency and provide customers with improved experiences.
Integration-centric BPM:
The main focus of Integration-centric BPM is to connect different systems and applications in an organization, thus providing a seamless flow. This type of BPM comes in handy especially for businesses functioning with multiple IT systems within complex environments.
The optimization data flow along with the automation process ensures smooth communication between various departments and technology. This helps in reducing manual errors leading to enhanced operational efficiency overall.
Document-centric BPM:
The focus of Document-centric BPM is on the effective management and streamlining of processes highly dependent on documents and content, such as contract administration, invoice handling, and compliance protocols.
The benefits to organizations include reduced paperwork volume, error minimization made possible by centralized document processing systems with automated workflows leading to improved adherence to regulatory stipulations.
Also Check: 11 best business automation ideas
Business Process Management System Features
Every organization seeking to boost efficiency, optimize workflows and stay competitive must rely on a potent Business Process Management (BPM) system. This article highlights the fundamental aspects that every BPM system should possess:
- Process Modeling:
To effectively design, visualize and document business processes, a BPM system must provide robust process modeling tools that feature intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces as well as flowcharts following Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standards. Such features allow both technical experts and layman users to craft precise process maps with ease.
- Workflow Automation:
In a BPM system, automation capabilities play a critical role. They enable the system to automate repetitive tasks and route them efficiently to the relevant individuals while ensuring that processes progress seamlessly from beginning to end without manual intervention. This helps minimize errors and speeds up task completion times.
- Integration Capabilities:
For a BPM system to be considered satisfactory, it should effortlessly integrate with the current IT infrastructure which includes important enterprise applications such as CRM and ERP. This guarantees that data can easily transfer across different systems thus increasing efficiency while minimizing silos in the organizational structure.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics:
Tools that enable real-time monitoring offer valuable insights on process performance, aiding managers in tracking progress and identifying bottlenecks so they can make informed decisions. Analytics should include customizable reports and dashboards featuring significant metrics such as key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Collaboration Tools:
Good BPM systems encourage teamwork among colleagues, offering task delegation, messaging capabilities, document sharing tools and collaborative workspaces. These features allow employees to collaborate effectively regardless of where they are located to achieve efficient results.
- Customization and Flexibility:
Customizability is essential for a BPM system as each organization possesses individualized processes and requirements. It should grant users the ability to personalize workflows, forms, and regulations according to their unique needs. This adaptability guarantees that the system can conform itself in response changes within diverse business environments.
- Security and Compliance:
To safeguard information and maintain regulatory compliance, it is critical to have security features. A BPM system must include data encryption, user authentication, audit trails and role-based access control measures so as to protect sensitive data in accordance with industry standards.
- Mobile Access:
In the world of mobile dominance, an effective BPM system must provide convenient access through smartphones or tablets. This empowers users to engage with processes and carry out tasks while on-the-go, facilitating flexibility in operations and ensuring uninterrupted progress even when employees are remote.
- User-Friendly Interface:
For the BPM system to gain broad acceptance, having an interface that is intuitive and easy-to-use is critical. Users should be able to navigate through menus with ease while being presented with clear instructions and icons that make interacting with the system straightforward and uncomplicated.
- Scalability:
As enterprises expand, their BPM requirements will mature. A flexible BPM platform can manage growing amounts of information and users while maintaining optimal performance, ensuring the system’s efficiency as the organization grows.
- Process Optimization:
Sophisticated BPM systems provide tools for process optimization that employ data and analytics to detect areas in need of improvement. By recommending enhancements, such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, and superior overall performance; these tools can assist with streamlining operations.
- Customer Support and Training:
To ensure dependability, a BPM platform ought to provide comprehensive customer service and educational materials. It should encompass helpful tutorials, user manuals as well as an efficient support squad that’s available to aid with problem-solving and streamlining processes.
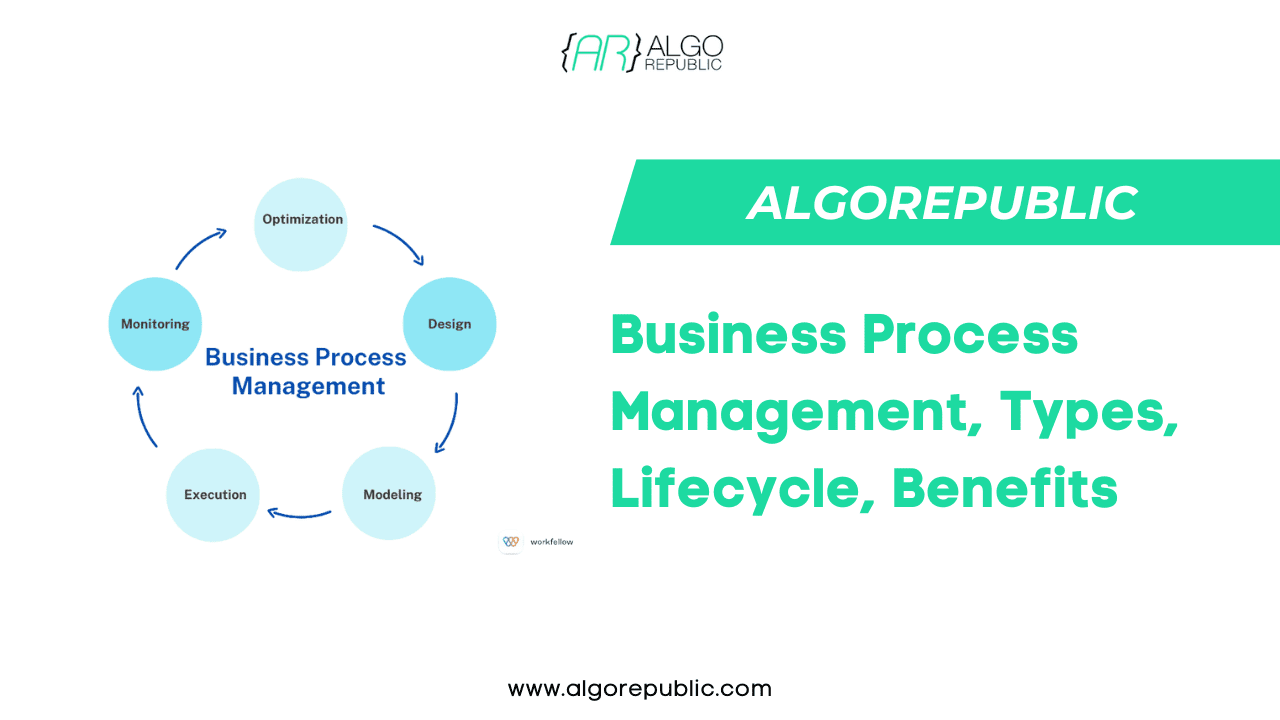
Business Process Management Flow
The BPM lifecycle consists of several interconnected stages:
Design: In the business process management design phase, companies evaluate their existing processes and pinpoint areas for improvement. They employ modeling methods like flowcharts or BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) to establish optimal procedures that are more streamlined.
Modeling: After designing the processes, they undergo modeling through BPM software or tools to generate graphic illustrations that stakeholders can readily comprehend and evaluate.
Execution: In order to execute the designed processes, one may use BPM software or automation tools, and depending on the complexity of these systems some manual interventions may be required.
Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of BPM is essential in business process management as it allows for close examination of process performance. This helps in the identification and resolution of issues while enabling businesses to track relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) for BPM. Through optimal processes, organizational objectives can be met with confidence.
Optimization: Processes are continuously optimized for increased efficiency, cost reduction and improved customer satisfaction with BPM on the basis of insights gathered from monitoring.
Why you need Business Process Management
Businesses looking to adapt BPM can experience various benefits. Some of the benefits of using Business Process management might include:
Increased Efficiency: Optimizing workflows and automating repetitive tasks are achievable for businesses through the utilization of BPM. It also helps in automating time consuming activities with BPM to boost overall operational efficacy.
Enhanced Agility: The streamlining and refining of business processes with BPM can help organizations to quickly adapt to waves in customer demands, market trends, and regulatory mandates.
Cost Reduction: By implementation of BPM and process automation to remove inefficiencies, businesses can majorly lower costs as a result of less manual labor, errors, and operational overhead.
Improved Visibility: Organizations can use BPM to obtain real-time insights on process performance, enabling them to detect issues, monitor progress and adopt a data-driven approach with BPM while making decisions.
Compliance and Risk Management: With the implementation of standardized processes with BPM and provision of audit trails businesses can ensure regulatory compliance, while also reducing the risks associated with manual errors and inconsistent issues.
Read more: Retail supply chain challenges
Examples of Business Process Management
Various industries and business functions can benefit from the application of BPM. A few examples of popular use cases across some industries include:
Customer Onboarding: Improving the overall customer experience with BPM while bringing down time-to-value through an easy onboarding process.
Supply Chain Management: With the help of BPM, businesses can experience optimization in supply chain management to improve work interaction with suppliers, bring down lead times and improve inventory management.
Financial Processes: By automating financial processes including invoicing, budgeting, and expense management with the help of BPM technology, businesses can definitely experience improved perfection while simultaneously decreasing processing time.
Human Resources: Automating HR workflow and process including recruitment, performance management, and employee onboarding can bring betterment to efficiency and ensure compliance.
Customer Service: Automated workflows can be instituted to handle customer inquiries, along with utilizing BPM (business process management) for the purpose of enhancing service quality and efficiency. Additionally, these workflows can effectively address problems and escalate them as needed.
Summed up
To sum up, Business Process Management is an advanced technique that companies can utilize to enhance efficiency, agility and competitiveness in the current ever-changing business realm. Through embracing BPM essentials and utilizing technology proficiently, using business processes becomes simpler resulting in innovation-driven growth which could be sustained over time.
BPM can revolutionize your operational efficiency and facilitate customer satisfaction, regardless of whether you are a small startup or a big corporation.
Haven’t yet switched from manual workflows to a faster automated working environment? We are here to help you revolutionize your workflow with a custom automation solution perfectly tailored to your business needs. Contact AlgoRepublic today!